
The implementation of stacks is relatively easy. Undo removes your most recent change, and redo builds upon already existing changes.

Another good example of a data stack is the undo and redo function on a computer or text editor. Stacks are great for processing nested structures, so they are important for understanding recursion.Ī simple real-world application of a stack is reversing a string letter by letter. We use stacks to implement functions, parsers, expression evaluation, and some algorithms. Stacks are used in a variety of ways when we code.

This is called the Last In First Out (LIFO) or First In Last Out (FILO) ordering. The first plate placed in the stack (the plate at the bottom of the stack) will be the last one to be removed, and the plate added last would be the first to be removed. ToArray().Let us conceptualize stacks using a stack of plates placed in a box. Note that toArray(new Object) is identical in function to
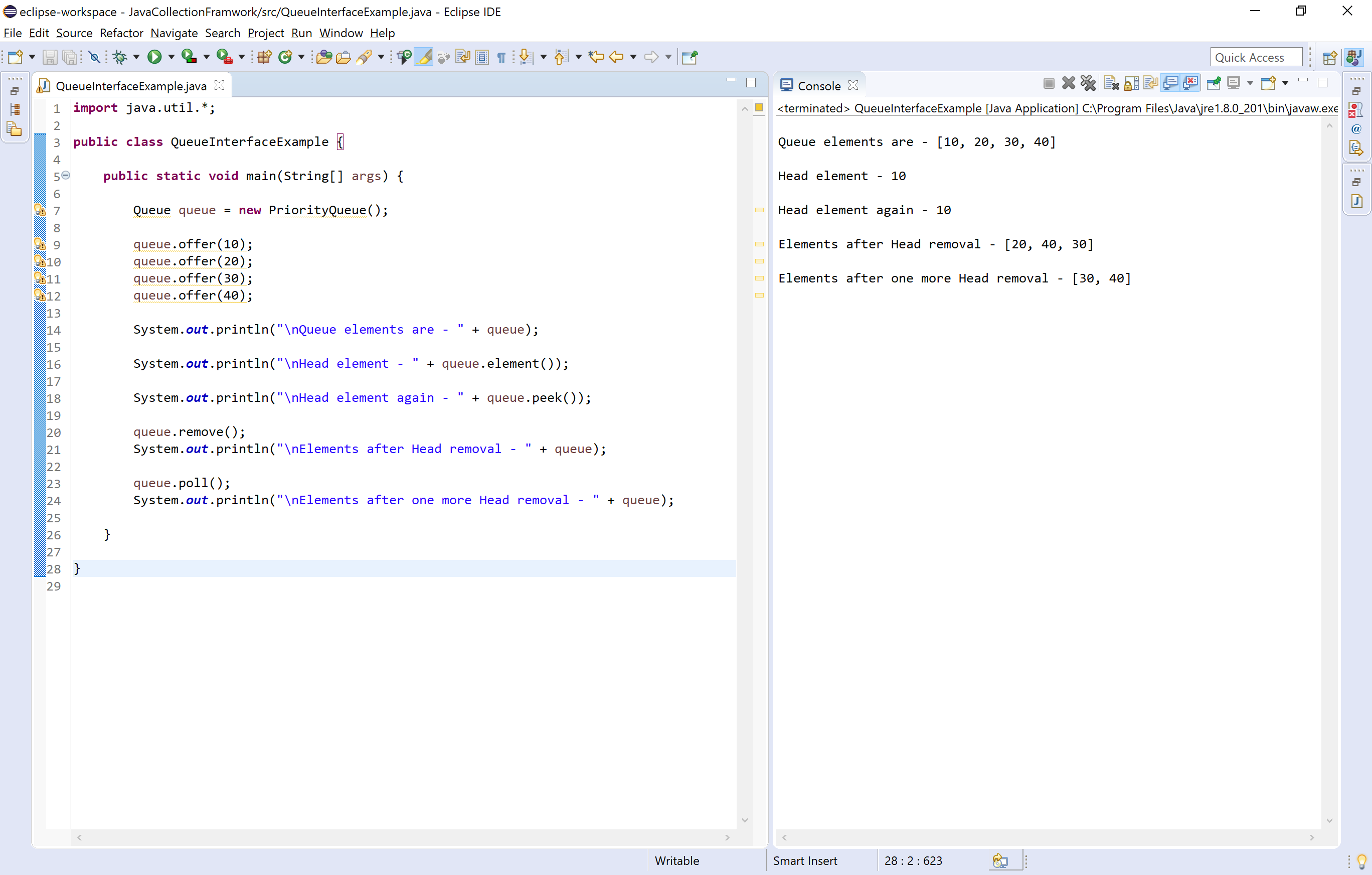
#Linked queue java code
The following code can be used to dump the queue into a newly Suppose x is a queue known to contain only strings. Under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs. Precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may, Like the toArray() method, this method acts as bridge betweenĪrray-based and collection-based APIs. The array immediately following the end of the queue is set to (i.e., the array has more elements than this queue), the element in If this queue fits in the specified array with room to spare Runtime type of the specified array and the size of this queue. Otherwise, a new array is allocated with the If the queue fits in the specified array, it Proper sequence the runtime type of the returned array is that of Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in The ConcurrentLinkedQueue in another thread. Memory consistency effects: As with other concurrentĬollections, actions in a thread prior to placing an object into aĪctions subsequent to the access or removal of that element from Methods of the Queue and Iterator interfaces. This class and its iterator implement all of the optional For example, an iterator operatingĬoncurrently with an addAll operation might view only some Inaccurate results if this collection is modified during traversal.Īdditionally, the bulk operations addAll, Of elements requires a traversal of the elements, and so may report
Because of theĪsynchronous nature of these queues, determining the current number Of the iterator will be returned exactly once.īeware that, unlike in most collections, the size method Elements contained in the queue since the creation They do not throw ConcurrentModificationException, and may proceed concurrently Reflecting the state of the queue at some point at or since theĬreation of the iterator. Iterators are weakly consistent, returning elements This implementation employs an efficient non-blockingĪlgorithm based on one described in Simple,įast, and Practical Non-Blocking and Blocking Concurrent QueueĪlgorithms by Maged M. Like most other concurrent collection implementations, this classĭoes not permit the use of null elements. Many threads will share access to a common collection. Operations obtain elements at the head of the queue.Ī ConcurrentLinkedQueue is an appropriate choice when The tail of the queue is that element that has been on theĪre inserted at the tail of the queue, and the queue retrieval The head of the queue is that element that has been on the This queue orders elements FIFO (first-in-first-out). An unbounded thread-safe queue based on linked nodes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
